Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Galaxy Size Distributions¶
This example demonstrate how to sample sizes for early and late type galaxies in SkyPy.
Size-Magnitude Relation¶
In Shen et al. 2003 [1], the observed sizes, \(R\), of galaxies were shown to follow simple analytic relations as a function of their absolute magnitudes, \(M\). For early-type galaxies, their mean radius follows Equation 14:
with \(a\) and \(b\) fitting constants. Likewise, late-type galaxies follow Equation 15:
The dispersion on these relations is given by Equation 16:
where \(\alpha\), \(\beta\), \(\gamma\), \(\sigma_1\), \(\sigma_2\) and \(M_0\) are fitting parameters.
In SkyPy, we can sample physical sizes for each galaxy type from lognormal distributions,
with median \(\bar{R}\) and width \(\sigma_{ln R}\), using the functions
skypy.galaxies.morphology.early_type_lognormal_size() and
skypy.galaxies.morphology.late_type_lognormal_size().
In this example, we simulate the sizes of galaxies with random magnitudes using the values for the parameters given in Shen et al. 2003 Table 1 [1] :
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skypy.galaxies.morphology import (early_type_lognormal_size,
late_type_lognormal_size)
# Parameters for the late-type and early-type galaxies
alpha, beta, gamma = 0.21, 0.53, -1.31
a, b = 0.6, -4.63
M0 = -20.52
sigma1, sigma2 = 0.48, 0.25
# SkyPy late sample
M_late = np.random.uniform(-16, -24, size=10000)
R_late = late_type_lognormal_size(M_late, alpha, beta, gamma, M0, sigma1, sigma2).value
# SkyPy early sample
M_early = np.random.uniform(-18, -24, size=10000)
R_early = early_type_lognormal_size(M_early, a, b, M0, sigma1, sigma2).value
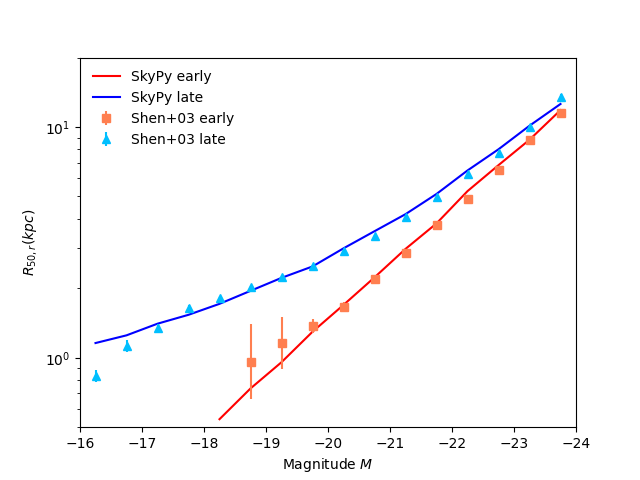
Validation against SDSS Data¶
Here we reproduce Figure 4 from [1], comparing our simulated galaxy sizes
against observational data from SDSS. You can download the data files for
early-type and
late-type SDSS
galaxies which have the following columns: magnitudes, median radius, minus
error, and plus error.
# Load data from figure 4 in Shen et al 2003
sdss_early = np.loadtxt('Shen+03_early.txt')
sdss_late = np.loadtxt('Shen+03_late.txt')
error_late = (sdss_late[:, 2], sdss_late[:, 3])
error_early = (sdss_early[:, 2], sdss_early[:, 3])
# Bins for median radii
M_bins_late = np.arange(-16, -24.1, -0.5)
M_bins_early = np.arange(-18, -24.1, -0.5)
# Center bins
center_late = (M_bins_late[:-1] + M_bins_late[1:]) / 2
center_early = (M_bins_early[:-1] + M_bins_early[1:]) / 2
# Median sizes for SkyPy late- and early-type galaxies
R_bar_early = [np.median(R_early[(M_early <= Ma) & (M_early > Mb)])
for Ma, Mb in zip(M_bins_early, M_bins_early[1:])]
R_bar_late = [np.median(R_late[(M_late <= Ma) & (M_late > Mb)])
for Ma, Mb in zip(M_bins_late, M_bins_late[1:])]
# Plot
plt.plot(center_early, R_bar_early, 'r', label='SkyPy early')
plt.plot(center_late, R_bar_late, 'b', label='SkyPy late')
plt.errorbar(sdss_early[:, 0], sdss_early[:, 1], yerr=error_early, color='coral',
marker='s', label='Shen+03 early', ls='none')
plt.errorbar(sdss_late[:, 0], sdss_late[:, 1], yerr=error_late, color='deepskyblue',
marker='^', label='Shen+03 late', ls='none')
plt.ylim(5e-1, 2e1)
plt.xlim(-16, -24)
plt.xlabel('Magnitude $M$')
plt.ylabel('$R_{50,r} (kpc)$')
plt.legend(frameon=False)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.show()
References¶
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.241 seconds)