Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Schechter Luminosity Function¶
This example demonstrates how to sample galaxies from a general Schechter luminosity function as implemented in SkyPy.
Joint Redshift-Magnitude Distribution¶
The number density of galaxies \(N\) with luminosities \(L\) in a cosmic volume \(V\) is widely observed to follow the Schechter luminosity function \(\phi\):
In SkyPy we reparameterise this distribution in terms of the absolute magnitude \(M\) of each galaxy:
In general, \(\phi_*\), \(M_*\) and \(\alpha\) can be redshift
dependent, resulting in a joint redshift-magnitude distribution
\(\phi(M, z)\). In SkyPy, sampling from this joint distribution is
implemented in skypy.galaxies.schechter_lf() where both phi_star and
m_star can be either constants or functions of redshift. In this example,
we follow a common parameterisation where phi_star and m_star are
exponential and linear functions of redshift respectively. Samples are
generated for a given sky_area and over a given redshift range z_range up
to a limiting apparent magnitude mag_lim with shot noise. The values of the
parameters are taken from the B-band luminosity model for star-forming
galaxies in López-Sanjuan et al. 2017 [1].
from astropy.cosmology import FlatLambdaCDM
from astropy.modeling.models import Linear1D, Exponential1D
from astropy.table import Table
from astropy.units import Quantity
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from skypy.galaxies import schechter_lf
z_range = np.linspace(0.2, 1.0, 100)
m_star = Linear1D(-1.03, -20.485)
phi_star = Exponential1D(0.00312608, -43.4294)
alpha, mag_lim = -1.29, 30
sky_area = Quantity(2.381, "deg2")
cosmology = FlatLambdaCDM(H0=70, Om0=0.3)
redshift, magnitude = schechter_lf(z_range, m_star, phi_star, alpha,
mag_lim, sky_area, cosmology, noise=True)
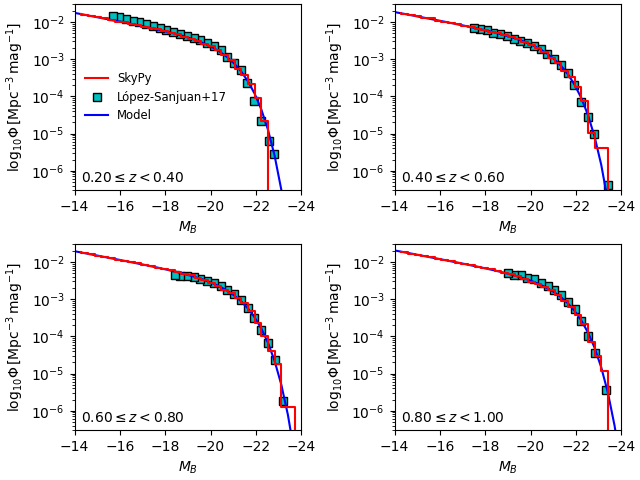
ALHAMBRA B-Band Luminosity Function¶
Here we compare our sampled galaxy B-band magnitudes in four different
redshift slices to the observed B-band magnitude distribution of
star-forming galaxies in the ALHAMBRA survey and the median-redshift
model from López-Sanjuan et al. 2017. The data file can be downloaded
here.
data = Table.read("lopez_sanjuan+17_B1.ecsv", format='ascii.ecsv')
fig, ((a1, a2), (a3, a4)) = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, constrained_layout=True)
bins = np.linspace(-24, -14, 35)
z_slices = ((0.2, 0.4), (0.4, 0.6), (0.6, 0.8), (0.8, 1.0))
for ax, (z_min, z_max) in zip([a1, a2, a3, a4], z_slices):
# Redshift grid
z = np.linspace(z_min, z_max, 100)
# SkyPy simulated galaxies
z_mask = np.logical_and(redshift >= z_min, redshift < z_max)
dV_dz = (cosmology.differential_comoving_volume(z) * sky_area).to_value('Mpc3')
dV = np.trapz(dV_dz, z)
dM = (np.max(bins)-np.min(bins)) / (np.size(bins)-1)
phi_skypy = np.histogram(magnitude[z_mask], bins=bins)[0] / dV / dM
# ALHAMBRA Survey star-forming galaxies (López-Sanjuan et al. 2017)
M_data = data[f'MB_{z_min:.1f}_{z_max:.1f}']
phi_data = 10 ** data[f'phi_{z_min:.1f}_{z_max:.1f}']
# Median-redshift Schechter function
L = 10 ** (0.4 * (m_star(z) - bins[:, np.newaxis]))
phi_model_z = 0.4 * np.log(10) * phi_star(z) * L ** (alpha+1) * np.exp(-L)
phi_model = np.median(phi_model_z, axis=1)
# Plotting
ax.step(bins[:-1], phi_skypy, where='post', label='SkyPy', color='r', zorder=3)
ax.plot(M_data, phi_data, 's', mfc='c', mec='k', label='López-Sanjuan+17')
ax.plot(bins, phi_model, label='Model', color='b')
ax.text(-14.3, 5e-7, r'${:.2f} \leq z < {:.2f}$'.format(z_min, z_max))
ax.set_xlabel(r'$M_B$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'$\log_{10} \Phi \, [\mathrm{Mpc}^{-3} \, \mathrm{mag}^{-1}]$')
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_xlim([-14, -24])
ax.set_ylim([3e-7, 3e-2])
a1.legend(loc=6, fontsize='small', frameon=False)
plt.show()
References¶
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.096 seconds)